Workflows¶
End-to-end workflows orchestrating ubFlow agents.
Last Updated: 2026-02-15
Level 0: Stakeholder Needs (WHY)¶
Workflow Stakeholder Needs¶
Stories describing the end-to-end workflows that orchestrate ubFlow agents.
Last Updated: 2026-02-06
As a developer, I want to follow a defined workflow (Change → Implement → Verify → Memory) to evolve my specifications and code, so that every change is analyzed, implemented with traceability, verified, and captured in project memory. Acceptance Scenarios:
|
As a developer, I want to run independent consistency checks on my specifications at any time (horizontal MECE review, vertical traceability), so that I can validate specification quality outside of a change workflow. Acceptance Scenarios:
|
As a ubFlow maintainer, I want to follow a defined release workflow that bundles multiple changes into a versioned release (Version → Validate → Publish), so that I can release stable, tested versions covering multiple changes. Acceptance Scenarios:
|
Level 1: Requirements (WHAT)¶
Workflow Requirements¶
Requirements for the end-to-end workflows that orchestrate ubFlow agents.
Last Updated: 2026-02-06
Description: ubFlow SHALL define a change workflow with the following sequence:
After @memory completes, the user SHALL be offered to either start a new change workflow or proceed to a release. Rationale: A defined sequence ensures consistent change processing. Each step produces output that the next step consumes, creating a pipeline with clear handoff points. The exit point after @memory supports iterative development (multiple changes) before bundling into a release. Acceptance Criteria:
|
Description: ubFlow SHALL support independent quality checks that can be invoked at any time without requiring a Change Document:
Rationale: Quality checks should be usable both during change processing (integrated) and as standalone tools (independent). This enables proactive quality management. Acceptance Criteria:
|
Description: ubFlow SHALL define a release workflow that bundles multiple changes:
Rationale: A release aggregates multiple changes into a distributable version. Unlike the change workflow (per-change), the release workflow operates across changes. Acceptance Criteria:
|
Level 2: Design (HOW)¶
Agent Framework Design¶
Shared architectural patterns across all ubFlow agents.
Document Version: 0.2 Last Updated: 2026-02-06
Agent Workflow¶
Design: ubFlow implements a four-agent workflow for structured change management. Agent Responsibilities:
Workflow: User Request
│
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ change │ ──→ Change Document + US/REQ/SPEC RST updates
└─────────────┘
│
▼ (approved)
┌─────────────┐
│ implement │ ──→ Code + Scripts + Tests (reads SPECs from Change Doc)
└─────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ verify │ ──→ Verification Report
└─────────────┘
│
▼ (passed)
┌─────────────┐
│ memory │ ──→ Updated copilot-instructions.md
└─────────────┘
│
▼
┌──────────┬──────────┐
│ change │ release │ (user decides)
└──────────┴──────────┘
Files:
VS Code Handoffs: Each agent file includes YAML frontmatter with Main Chain: change → implement → verify → memory
↑ │
├────────────────────────────┘ (next change)
│
└── or ──→ release (bundle changes)
Analysis Agents (bidirectional): mece ↔ trace
│ │
└───────┴──→ change (to fix issues)
Memory Agent: Invoked after verify. Hands off to change (for next change) or release (to bundle changes into a versioned release). Handoff Format: ---
description: Short agent purpose for UI display
handoffs:
- label: Display name
agent: ubFlow.targetagent
prompt: Default prompt text
---
Initial Prompt Recommendations: To show ubFlow agents as suggestions when opening a new chat, configure VS Code workspace settings: File: {
"chat.promptFilesRecommendations": {
"ubFlow.change": true,
"ubFlow.implement": true,
"ubFlow.verify": true,
"ubFlow.mece": true,
"ubFlow.trace": true,
"ubFlow.memory": true
}
}
This ensures users see ubFlow workflow options immediately. |
Prompt Architecture¶
Design: Strict separation between prompt files and agent files. Prompt Files (
Format: ---
agent: ubFlow.change
---
Agent Files (
Rationale:
|
Agent Interaction¶
Design:
All ubFlow agents use the When to Use ``ask_questions``:
When NOT to Use:
Format Reference: ask_questions({
questions: [{
header: "≤12 chars", // Quick-pick title, unique ID
question: "Full context", // Explains what is being decided
options: [
{ label: "Option A", description: "Brief detail" },
{ label: "Option B", description: "Brief detail", recommended: true }
],
allowFreeformInput: false // true when custom response is expected
}]
})
Rules:
Implementation via Skill File: The interaction pattern is consolidated in a skill file instead of being duplicated across agent files:
Example — Level Transition (Change Agent): ask_questions({
questions: [{
header: "Continue?",
question: "Level 1 is saved to the Change Document. Where do you want to continue?",
options: [
{ label: "Proceed to Level 2 (Design)", description: "Analyze design specs", recommended: true },
{ label: "Revise Level 1", description: "Go back and revise requirements" },
{ label: "Pause here", description: "Save progress and continue later" }
]
}]
})
|
Traceability¶
Stakeholder Needs¶
ID |
Title |
Status |
Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
End-to-End Change Workflow |
implemented |
mandatory |
|
Independent Quality Checks |
implemented |
high |
|
Release Workflow |
implemented |
mandatory |
Requirements¶
ID |
Title |
Status |
Tags |
|---|---|---|---|
Change Workflow Sequence |
implemented |
workflow; change; orchestration |
|
Independent Quality Check Workflow |
implemented |
workflow; quality; mece; trace |
|
Release Workflow Sequence |
implemented |
workflow; release; orchestration |
Design Specifications¶
ID |
Title |
Status |
Links |
|---|---|---|---|
Agent Interaction via Selection Menus |
implemented |
||
Prompt-Agent Separation |
implemented |
||
Four-Agent Workflow |
implemented |
REQ_WF_CHANGE_SEQUENCE; REQ_CHG_ANALYSIS_AGENT; REQ_CHG_IMPL_AGENT; REQ_CHG_VERIFY_AGENT; REQ_DX_MEMORY_AGENT; REQ_CHG_WORKFLOW_STEPS |
needflow Diagram¶
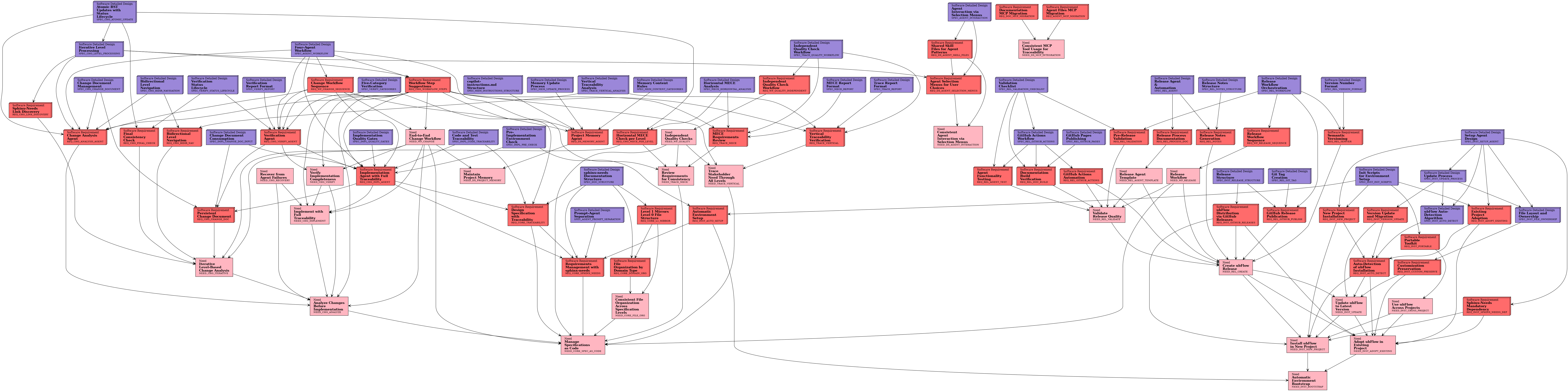
SPEC_AGENT_WORKFLOW¶